Clive Humby once said, "data is the new oil". Today, his statement is more true than ever. Companies all over the world can grow and expand their offer thanks to the proper use of data. And the discipline that's responsible for analysing data (i.a., for business purposes) is called data science. In this blog post, you will discover what data science is all about, what are the benefits of data science and how data science helps businesses. We hope this article will encourage you to rethink the data management strategy in your company.
Before we get down to specifics, let’s discuss what data science actually is and why it’s so vital in today’s world.
What is data science?
What is data science in simple words? If we had to coin one short definition, we’d say it’s a discipline that uses diverse techniques and algorithms (frequently based on machine learning) to extract information from big data (both unstructured and structured) and turn it into useful knowledge.
So, in other words, everything starts with big data. It’s a common term used to describe voluminous amounts of data that cannot be processed manually. Big data can consist of terabytes of information and has to be analysed and processed using automated tools and techniques. It would take hundreds of years for a single person to explore the big data manually.
In general, big data can be stored in different places and formats. The common division is based on its form. That’s why we talk about structured and unstructured big data. Structured big data is far easier to analyse, and it can be fitted into rows and columns (e.g., in an Excel file). Unstructured data cannot be fitted in such a limited form due to its multidimensionality. A good example of unstructured data are audio interviews with employees.
How data science helps business
Every large company processes gigabytes of information each day. It’s all just a matter of gathering all the available information and turning it into something useful. In big, international organisations, big data comes from:
- Marketing campaigns (Google Analytics alone is a vital source of marketing big data, and so are DXPs)
- Website (activity on the website, most clicked links and subpages, time spent on browsing it, demographic data about visitors)
- Social media (posts, comments, interactions, mentions of your brand)
- Customer service (phone calls from customers, emails and messages received via the website and social media profiles)
- Sales (in big companies, CRM is a mine of knowledge for business)
- HR (received resumes, employee information)
- Finance and accounting (company’s financial data, revenue, costs, investments)
And the list goes on and on. In fact, every year, there are new communication channels and touchpoints that your company can use to up your sales and marketing game. Each of these channels generates new reserves of information. Moreover, here, we listed just data sources that come from within the company. There are also tons of information coming from the market and the world. For instance, if you run an online store, a vital part of external information revolves around prices in your competitors’ stores. If you manage air traffic, you have to be non-stop informed about the weather conditions. And if you're a manufacturer of jewellery, you are surely interested in the prices and availability of gold. All of that is also big data!
As you can see, data scientists have a lot on their plates, and the amount of information to gather and analyse to drive valuable insights can be overwhelming.
BENEFITS OF DATA SCIENCE
We want to show you five applications of data science. Of course, the way you can use data analytics differs based on the scale and form of your business. The niche that you operate in is also crucial. But we tried to mention universal applications.
Improve dialogue with your customers The online world is just filled with information about your customers. Purchase history, product searches and queries, social media comments, brand mentions – it all can be used to understand what your customers want and need. Data analytics is a foundation that enables customer segmentation, personalisation campaigns, cross-selling, upselling and many other techniques that help you make more money. The more you know about customers, the more accurately you can respond to their needs and, this way, get their interest and engagement.
Better marketing campaigns Data science can also help you with marketing. Today, we frequently talk about data-driven marketing. In this approach, everything you do is backed by solid data analysis. With data-driven marketing, you can:
- Reach target audience effectively and accurately (so-called highly-targeted campaigns)
- Introduce automation and personalisation in your campaigns
- Select the most effective marketing tools and channels and focus on them
- Optimize marketing budget spent
- Tailor brand experiences to the needs of your customers and current trends (according to Think with Google, 61% of people expect brands to tailor experiences based on their preferences[1])
- Improve product and offer development processes
New product development Data analytics has also revolutionised new product development. Companies can use it to collect and analyse customer feedback and opinions to minimise the risk involved in every new product. With a thorough analysis of your target audiences, it's far easier to develop a new product or service that will match your customers' preferences.
Furthermore, through so-called predictive analytics (which is a subsection of data science), businesses can foresee the potential performance of their future products in the market and optimise their marketing strategies to attract potential customers.
As we all know, new product development is a time-consuming and complex endeavour. You start with research and the initial conception of your product. Then you test your idea, produce a prototype, and when you’re sure there is a demand for your new product – you take it to the production stage. Data science can help you all along the way. And the stakes are high; if you neglect research and analysis, there is a huge risk that your product will fail.
According to Harvard Business School, there are over 30,000 new products introduced every year, and 95% of them fail[2].
One of the ways to avoid this dark scenario is to implement data science and analyse and test everything you do before you start production.
Enhanced supply chain management
We live in difficult times for companies that rely on international supply chains. According to US Census Bureau, the inventory-to-sales ratio in the United States has never been lower:
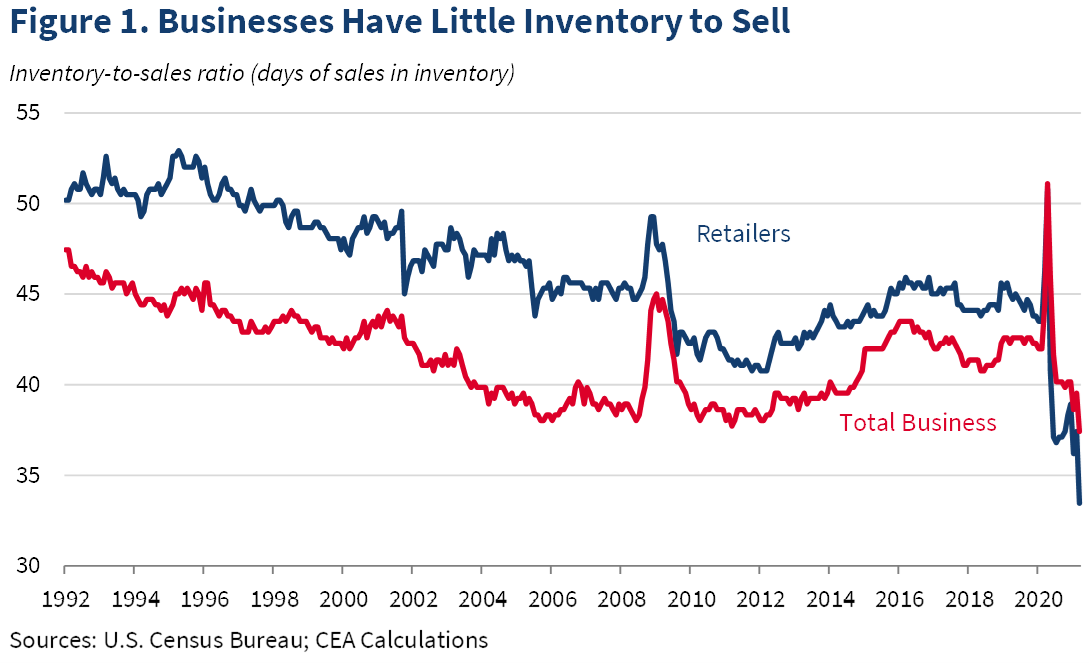
Of course, data science is not some kind of a magic wand that will make covid-19 and all the inventory-related problems go away. But it can help you plan and manage your supply chains more effectively, even will all these difficulties related to transporting and manufacturing products.
At this point, we need to answer a crucial question: Which supply chain processes can be streamlined using data science?
- Inventory management: with data science, you can forecast product demand and optimise your inventory levels accordingly so that you avoid the dead stock issue.
- Order fulfilment and tracking: last-mile delivery plays a critical role in customer satisfaction. With data science, you can optimise your processes, e.g., related to packing and sending parcels. As a result, customers will get their orders quicker.
- Smart maintenance: retail and transport companies use various machines, devices and vehicles in their everyday work. Data science can help your company assess the condition of each such machine, predict possible failures and plan maintenance accordingly to avoid them.
Sourcing and screening candidates The last application comes from the HR world. Nowadays, you have access to smart tools that help your company source, screen and select the most promising candidates. After all, it’s all based on finding the best candidate source, optimising your job ads and screening hundreds of received resumes. Here, almost 100% of work can be automated and executed by intelligent algorithms that use AI and data science. Let’s go further; there are even smart tools that will automatically schedule a job interview with selected candidates! It’s a huge work simplification for your recruiters.
One of such tools is Olivia, created by Paradox AI. Olivia can help HR departments with:
- Answering questions about the workplace and job ad
- Collecting resumes from candidates
- Selecting the best candidates
- Scheduling job interviews with them
Of course, there are many more applications of data science and not just in marketing, HR and customer service departments. You can use smart tools that use data analytics to automate and streamline almost everything you do in your organisation. That’s what makes this tool so efficient and versatile.
Lastly, we want to mention something relatively new, which is called small and wide data.
NEW TREND: SMALL AND WIDE DATA
These are two new approaches to data science that enable more robust analytics. In small data, you concentrate on time-series analysis and supervised machine learning, so you need fewer data to achieve similar results. And what about wide data? This term describes the effect of synergy that can be achieved thanks to the analysis of all data, both structured and unstructured, in all forms and formats. According to Gartner’s predictions, 70% of organisations will shift their focus from big to small and wide data by 2025[3].
Big data vs. data science: What are the differences between them?
Lastly, we want to answer two frequent questions. Are big data and data science the same thing? Obviously, not. Big data is simply a large collection of information. No more, no less. Data science tries to take that collection of information and use it to get useful business-wise insight. So big data is a piece of wood, and data science is a woodworker.
Additionally, there is also something called business intelligence. Here, the difference is less apparent. In general, both these disciplines are about the same thing – getting valuable information from the data. However, data science frequently concentrates on the future. It facilitates the decision-making process. On the other hand, business intelligence is more descriptive. It focuses on what already happened and why. Of course, this knowledge can also be used in future decisions, but BI looks at big data from a slightly different angle.
Is a data scientist job similar to a data analyst job?
And that's the second question that often arises. Again, there are a lot of similarities. Both these professions work with big data; both want to drive useful insights from it. But data scientists concentrate on the future. They analyse trends and patterns in data in order to find out what can happen in the future. Data analysts simply analyse data and nothing more. In large companies that work with big data, both professions are important, and they come in handy in different situations.
We hope that now your knowledge about data science is more comprehensive and organised. If you want to start using data science in your company, we encourage you to contact our team. Schedule a free consultation and tell us about your ideas. We will gladly help you execute your vision and take your company’s operation to a whole new level using data science and related disciplines.
[1] thinkwithgoogle.com/marketing-strategies/data-and-measurement/data-driven-marketing-statistics/ [2] inc.com/marc-emmer/95-percent-of-new-products-fail-here-are-6-steps-to-make-sure-yours-dont.html [3] gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2021-05-19-gartner-says-70-percent-of-organizations-will-shift-their-focus-from-big-to-small-and-wide-data-by-2025
Author

Paweł Strąg
Chief Technology Officer
The last 4 years of Pawel’s 18-year IT career has been spent exclusively on cloud platforms. He has a proven track record of delivering effective solutions for large enterprises and is currently involved in developing a highly-accurate cloud computing platform supporting wind energy calculations for wind turbines.
Related articles
![A well-crafted prompt doesn’t just work once. It works across teams, channels, and campaigns. It can be tweaked for new use cases and refined based on what performs best.]()
June 27, 2025 / 4 min read
Prompts are marketing assets: how to reuse, and scale them
Prompts aren’t throwaway lines. They’re repeatable, scalable assets that can streamline your marketing your team’s output. Learn how to build a prompt library that delivers.
![Woman using a wheelchair in the office settings]()
June 17, 2025 / 5 min read
What is accessibility and why it matters?
Accessibility ensures everyone — including those with disabilities or limitations — can read, navigate, and engage with your content equally.



